Warehouse automation stands at the intersection of technology, logistics, and innovation. As global commerce has expanded, the pressure on warehouses to handle increasing volumes of goods efficiently has never been greater. Beyond just responding to labor shortages and supply chain challenges, the evolution of warehouse automation also caters to the rising consumer expectations for faster deliveries and impeccable service.
Further, with advancements in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things (IoT), these systems have become smarter, more adaptable, and more integrated. They can now predict and respond to dynamic changes in demand, reduce downtimes, and optimize resources in real-time. Moreover, as sustainability becomes a pressing concern, automated warehouses offer eco-friendly solutions by reducing waste and energy consumption.
The versatility and adaptability of these systems mean that they cater to both large-scale warehouses and smaller storage facilities. With a broad spectrum of applications and tools, warehouse automation is truly transforming the way businesses operate. Dive in as we delve into some of the most prominent examples of warehouse automation technologies.
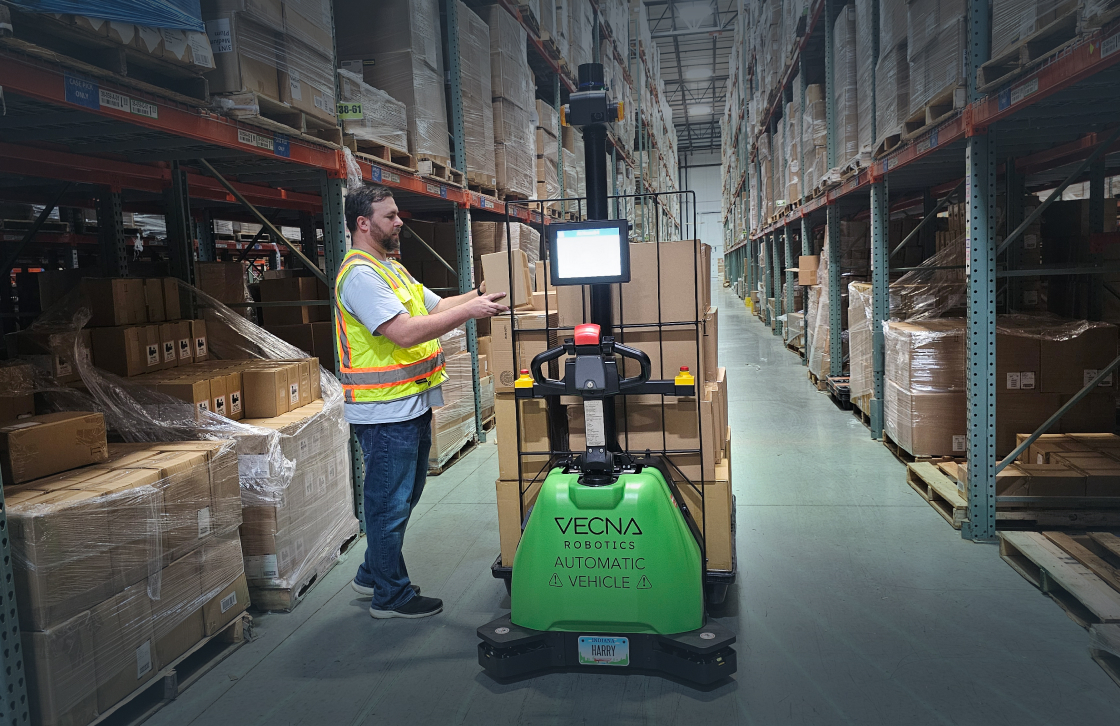
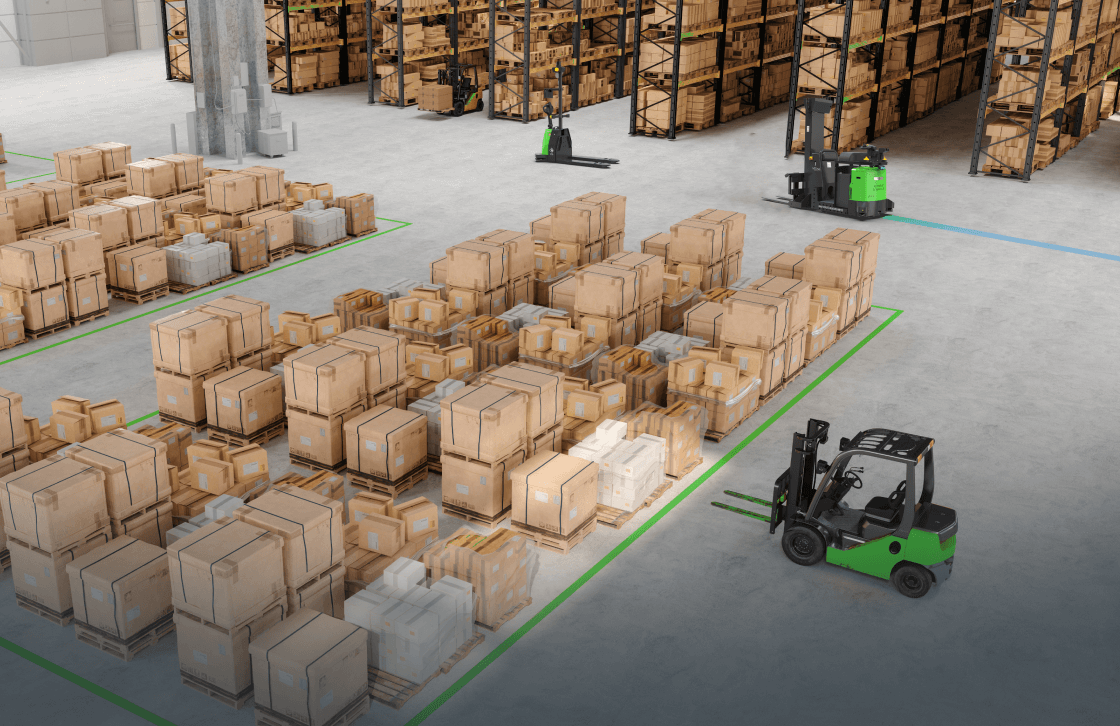
Automatic Guided Vehicles (AGVs): At the heart of modern warehousing are these ingenious machines – AGVs. As their name suggests, these vehicles are programmed to operate autonomously, eliminating the need for constant human oversight. They are equipped with sensors and onboard navigation systems, enabling them to maneuver through complex warehouse layouts and avoid obstacles. AGVs can be programmed to follow specific routes, and they play a pivotal role in tasks such as transporting goods from storage areas to dispatch zones, supplying materials to specific production lines, and automating the process of loading and unloading goods from trucks and trailers.
The potential of AGVs extends beyond the confines of warehouses. McKinsey predicts a future where autonomous vehicles, including AGVs and drones, will be responsible for delivering a staggering 80% of all items. The concept of drone deliveries, which once belonged to the realm of science fiction, is fast becoming a reality. Companies are fervently exploring the potential of drones for last-mile delivery – the final step in the delivery process, which is often the most complex and costly. Walmart, a retail behemoth, has been especially proactive in this domain. They outpaced competitors, including Amazon, by successfully completing over 6,000 drone deliveries in 2022 alone. On the other hand, Amazon, which has often been at the forefront of technological innovation, only initiated its drone delivery program in December of the same year. The race to automate and innovate in the warehousing and delivery sector is truly on, with AGVs and drones playing leading roles.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS): Integral to modern warehouse optimization, ASRS combines the precision of technology with the practicality of efficient space utilization. These systems typically consist of automated cranes or robotic arms, which play a vital role in accurately storing or retrieving products from designated warehouse locations. Their operations range from handling bulky pallets to dealing with smaller cases or individual items. Depending on the warehouse’s design and requirements, ASRS can be tailored to interact with various storage setups, such as high-rise racks, multi-tiered shelves, or compact storage containers.
As the e-commerce sector surges, the demand for swift and efficient warehousing solutions is more pronounced than ever. Modern ‘fulfillment centers,’ essentially evolved warehouses, are brimming with robotic solutions, sophisticated lifting equipment, and dynamic sorting systems. These technological marvels aim to expedite product handling and inventory management. Companies like Amazon have pioneered the adoption of these solutions, setting industry standards. Parallelly, in the UK, online grocery retailer Ocado is pushing the boundaries with its automated racking systems. These systems are not merely about swift product retrieval; they’re backed by a wealth of data analytics. By collecting and analyzing data across their supply chain, companies like Ocado can fine-tune operations, forecast demands, and ensure that the customer receives their order in the shortest time possible. The marriage of robotics with data analytics in warehouses is shaping a new era of efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Pick-to-light and Put-to-light systems: At their core, these systems employ visual cues, mainly lights and digital displays, to guide warehouse workers swiftly and correctly to product locations, eliminating the need for paper lists or frequent checks on handheld devices.
The brilliance of these systems lies in their simplicity. When a worker approaches a shelving unit or storage area, the relevant light indicator illuminates, pinpointing the exact item to be picked. This not only speeds up the retrieval process but also significantly reduces the chances of picking errors, a common pain point in manual operations. Conversely, Put-to-Light works similarly, guiding workers on where to place or restock items.
Diving deeper into their functionality, these systems are often integrated with the warehouse’s central management software. This integration means that as orders are processed, the system immediately translates them into visual cues for the workers. The real-time nature of this system ensures that even last-minute orders can be processed without significant delays.
Additionally, the flexibility of Pick-to-Light and Put-to-Light systems is noteworthy. Whether a warehouse utilizes traditional shelving, high-density racking, or carousel storage, these systems can be tailored to fit seamlessly. Given the rising demand for same-day or next-day deliveries in the e-commerce sector, such systems become critical assets, allowing warehouses to handle a higher volume of orders without compromising accuracy.
The data generated from these systems also provides invaluable insights into warehouse operations. By analyzing pick rates, error frequencies, and worker efficiency, managers can make informed decisions, leading to continuous optimization of processes and, ultimately, a better bottom line.
RFID technology and barcode scanning: Both these technologies play a pivotal role in the modern-day warehousing ecosystem, serving as the backbone of inventory management and tracking.
RFID (Radio-Frequency Identification) is a step ahead of the traditional barcode system. Unlike barcodes, which need direct line-of-sight to be scanned, RFID tags can be read from a distance and even through materials, drastically reducing the time it takes to process items. This becomes especially valuable in bulk processing or when items are stacked in a manner that hides their barcodes. Moreover, RFID tags can store more information than barcodes, providing insights like origin, expiration date, and even handling instructions.
Barcode scanning, on the other hand, remains the gold standard in many warehouses due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of implementation. While it might seem rudimentary, advancements in barcode technology have enabled faster scanning, better accuracy, and integration with sophisticated warehouse management systems. When paired with technologies like ASRS and pick-to-light systems, barcode scanning helps streamline the picking and storing process, reducing errors and improving overall efficiency.
The fusion of RFID and barcode scanning in a single system also offers warehouses the best of both worlds. Such hybrid systems facilitate adaptive inventory tracking – using barcodes for general items while employing RFID for high-value or sensitive goods. This layered approach to tracking ensures optimal resource allocation, making the most of the benefits of each technology while minimizing their respective limitations.
Robotics and drones: These technological marvels are revolutionizing the warehousing landscape by taking on an array of tasks, previously executed by manual labor. While robots excel in areas like palletizing, packing, and kitting, drones are soaring new heights in inventory management, overhead surveillance, and even order fulfillment by navigating hard-to-reach areas.
Global retailers such as Walmart and Target are at the forefront of this change, leveraging autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) to optimize operations, navigate warehouse floors more efficiently, and dramatically cut labor costs. E-commerce colossus, Alibaba, on the other hand, is harnessing the power of automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to swiftly transport goods within its vast warehousing facilities. Beyond retail and e-commerce, the automotive industry is also catching up. BMW, for instance, is integrating robotic systems not just for heavy lifting but also for intricate tasks like handling delicate car parts and facilitating precise assembly of components.
It’s also worth mentioning, that the integration of these technologies is not just about efficiency. It’s also about creating safer work environments. Robotics and drones reduce the need for human intervention in potentially hazardous tasks, such as lifting heavy objects or reaching high shelves, ensuring a safer workplace and reducing injury-related downtimes.
Conveyor systems: For decades, conveyors have been the backbone of many warehouses, streamlining the flow of goods from one point to another with minimal manual intervention. These mechanized systems are particularly vital in larger facilities where distances between various departments, like receiving and shipping, can be vast. Conveyor systems can range from simple belt-driven setups to more complex arrangements, such as roller conveyors, chain conveyors, and vertical conveyors that can elevate products to different warehouse levels.
Incorporating advancements in technology, modern conveyor systems can be integrated seamlessly with various other warehouse automation mechanisms. Barcode scanners, for instance, can be paired with conveyors to instantly identify and sort products, directing them to appropriate sections or processing units of the warehouse. Similarly, sensors and advanced tracking systems ensure that the movement of products is closely monitored, reducing the chances of errors or misplacements.
The rise of e-commerce and the subsequent demand for rapid order fulfillment has given even more impetus to the importance of conveyors. As the need for quicker processing times becomes paramount, warehouses are leveraging high-speed conveyor systems, capable of moving products at unprecedented speeds while ensuring safety and reducing wear and tear.
Today’s conveyor systems are also increasingly being designed with flexibility in mind. Modular conveyor sections can be added or removed to adapt to changing operational needs. This adaptability is particularly beneficial during peak seasons or sales when the influx of orders can be unpredictable. Energy efficiency and reduced noise levels are other aspects that manufacturers are focusing on, ensuring that these systems are not just effective but also environmentally friendly and conducive to a better working environment.
Automatic packing and palletizing systems: Revolutionizing the end-of-line processes in warehouses, these systems bring speed, accuracy, and consistency to tasks that were traditionally manual and labor-intensive. By employing robotics and computer vision, automatic packing systems can adapt to different product sizes, shapes, and configurations, ensuring that each item is packed securely and efficiently. This adaptability is crucial in today’s diverse product environment, where a single warehouse might handle anything from tiny electronic components to bulky household items.
The advantages of such automation are manifold. Firstly, they drastically reduce the risk of human error in packing, ensuring that products are protected against potential damage during transportation. Secondly, these systems can function around the clock, resulting in higher throughput and meeting increased demand during peak periods.
Furthermore, advanced sensors within these systems can detect and adjust to varying product dimensions, selecting appropriate boxes or packing material, leading to reduced wastage and ensuring optimal space utilization within cartons or crates.
Palletizing systems, on the other hand, use robotic arms or specialized machinery to stack products onto pallets in predefined patterns. This ensures maximum stability during transport and optimal space utilization in storage or shipping containers. Integrated with conveyor systems, they form a seamless flow from the packing line right through to the shipping bay. And, when paired with barcode scanners or RFID technology, the packed and palletized goods can be immediately logged into inventory systems, providing real-time data on outgoing shipments, and enhancing transparency and traceability.
Voice-directed picking systems: A blend of cutting-edge voice recognition technology and human skill, these systems have been transforming the picking process in many modern warehouses. By providing workers with wireless headsets that receive real-time voice instructions on what items to pick and where to find them, these systems optimize picking routes, reduce the likelihood of picking errors, and increase overall efficiency.
What sets voice-directed picking apart from traditional methods is its hands-free, eyes-up approach. This allows workers to focus on the task at hand without the constant need to refer to paper lists or handheld devices. The result? Faster picking times and a reduction in errors.
And, because voice-directed systems can be integrated into a warehouse’s existing management software, they can continually adapt to changes in inventory levels, product locations, and even worker speed or proficiency. This means that as the warehouse evolves – whether that’s due to seasonal stock fluctuations, the introduction of new products, or changes in order layouts – the voice-directed system can adapt in real-time, offering consistent efficiency.
These systems also often come with multilingual support, accommodating a diverse workforce and ensuring clear communication regardless of language barriers. The ergonomic benefits shouldn’t be overlooked either. Without the need to handle devices or paper lists, workers can pick items more ergonomically, potentially reducing workplace strains and injuries.
Automated sortation systems: At the heart of streamlining warehouse operations lies the capability to swiftly and accurately sort through vast quantities of goods. Automated sortation systems, designed to enhance the categorization and dispatch of products, play a pivotal role in achieving this. Depending on the nature and scale of operations, warehouses can choose from a variety of sortation systems like the cross belt sorter, which rapidly shuttles items using conveyor belts; the tilt tray sorter, which carefully tilts to release items into designated chutes; or the bomb bay sorter, where compartments open simultaneously from the bottom to sort items.
These advanced systems have been a game changer for industries facing high volumes of diverse products. By automating sorting, errors are significantly reduced, throughput is increased, and manual labor is utilized more strategically. Integration capabilities further amplify their efficiency. For instance, when combined with barcode scanners or RFID technology, the real-time tracking and sorting of products becomes seamless.
Additionally, automated sortation systems can be calibrated for precision based on weight, size, destination, or any specific parameter set by the warehouse. As e-commerce continues its rapid growth trajectory, the importance of these systems becomes even more pronounced. They ensure that the right product reaches the right customer promptly, reinforcing customer trust and loyalty. As warehouses grow and product ranges diversify, the adaptability and scalability of automated sortation systems will be crucial for maintaining operational efficacy and meeting customer expectations.
Automated Guided Carts (AGCs): Within the intricate tapestry of warehouse automation, AGCs emerge as a more nimble counterpart to AGVs. Functionally similar, AGCs operate to transport materials and products within a warehouse setting without the need for human supervision. While both machines are designed for transporting goods, AGCs typically handle lighter loads, making them suitable for operations with tighter spaces or requiring more frequent stops.
These AGCs can be meticulously programmed to follow specific routes, ensuring efficient navigation through a facility’s labyrinthine pathways. Their applications don’t just stop at material movement. They’re particularly useful in scenarios such as supplying materials to production lines, shuttling tools in manufacturing setups, or facilitating just-in-time deliveries within interconnected factory processes.
A standout feature of AGCs is their adaptability. With evolving warehouse needs, their routes can be easily reprogrammed, granting operations the flexibility to adjust workflows as demand patterns shift. Furthermore, equipped with sensors and safety mechanisms, AGCs significantly reduce the risk of collisions, ensuring a safer work environment. As industries lean towards tighter production schedules and quicker turnaround times, AGCs are poised to be an indispensable asset, bridging gaps in the flow of materials and streamlining overall warehouse efficiency.
Whether you’re looking to transport goods from point A to point B without adding headcount to your warehouse team, or need automated support retrieving or sorting products, these examples of warehouse automation show the capabilities that robotics can bring to your facility.
If you’re ready to tap into the power of warehouse automation, set up an appointment with a Vecna Robotics automation expert today.