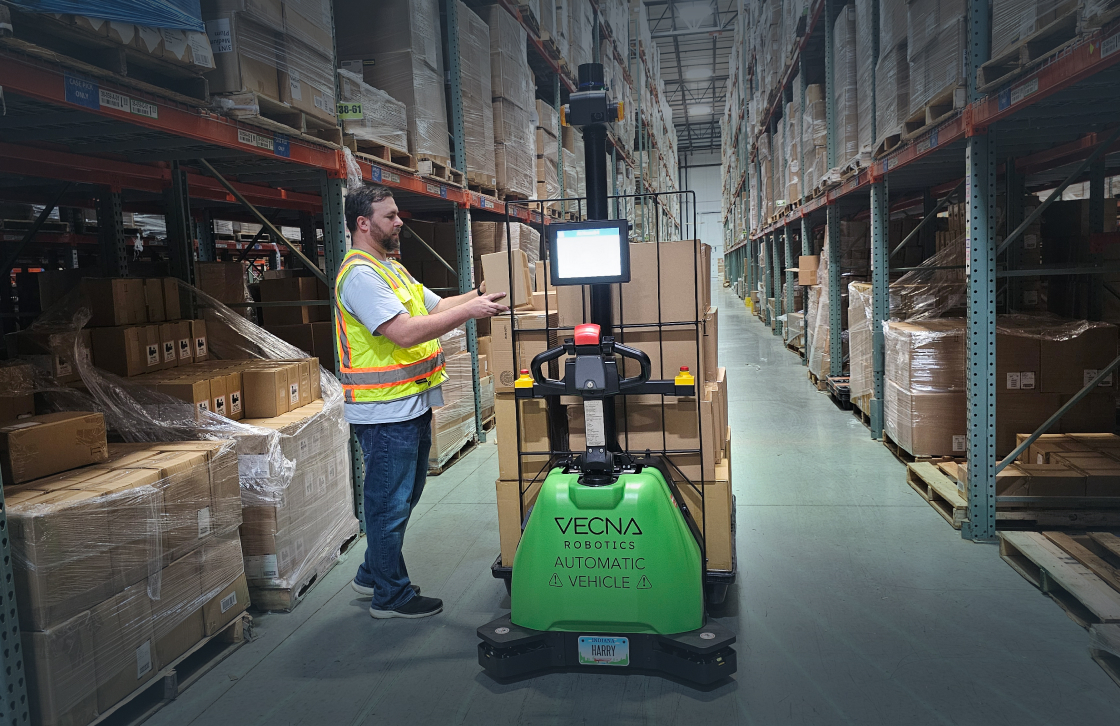
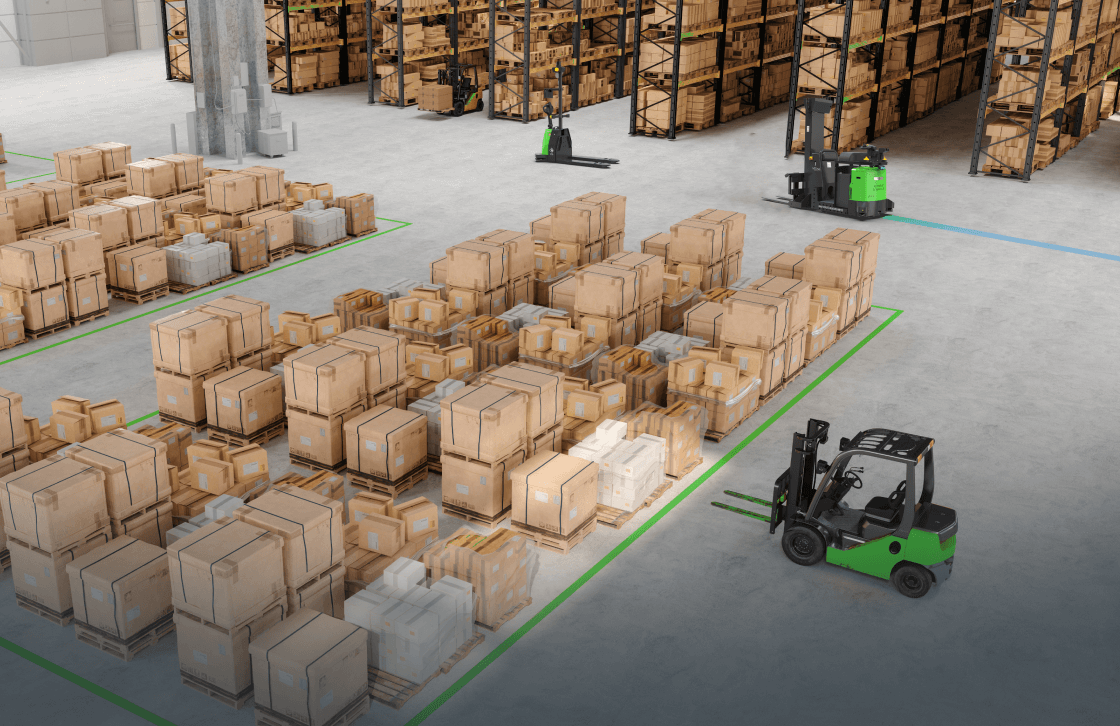
Logistics optimization with automation can be a game-changer for many businesses. In today’s fast-paced world, there’s an increasing demand for quicker, more reliable, and cost-efficient methods of transporting goods. As supply chains grow more complex, the old manual processes become cumbersome and prone to error. Logistics optimization with automation provides a solution to these challenges.
By employing advanced technologies and systems, businesses can streamline their operations, making them more agile and responsive to market demands. From utilizing automated tracking systems to employing AI-driven route optimization, there are numerous avenues through which businesses can harness the power of automation. Here are a few ways to achieve logistics optimization with automation:
- Automated routing and scheduling: Utilizing advanced software and algorithms, this method doesn’t just determine the best routes. It also considers external factors like traffic conditions, weather patterns, and delivery priority. This dynamic approach ensures that businesses can minimize fuel consumption and delivery times while optimizing vehicle utilization.
- Inventory management: Beyond simply tracking inventory levels, these automated systems provide predictive analysis based on historical data and market trends. This helps businesses anticipate demand, thereby minimizing both stockouts that can hinder sales and overstocking that ties up funds unnecessarily.
- Automated tracking and monitoring: It’s more than just knowing the location. Real-time automated tracking allows businesses to monitor the conditions of goods in transit, especially crucial for temperature-sensitive or fragile items. This level of oversight ensures product integrity and allows for prompt adjustments in case of unforeseen delays.
- Robotics and drones: These tools not only reduce the manual labor needed in logistics but also offer precision and speed. Drones, for instance, can swiftly deliver to hard-to-reach locations or during peak traffic times, circumventing traditional challenges.
- Machine learning and AI: Beyond merely analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can recognize patterns and draw insights humans might overlook. It can forecast future demand spikes or lulls, aiding businesses in preemptively adjusting their logistics strategies for maximum efficiency and customer satisfaction.
- Automated payments: Electronic payment systems don’t just simplify billing; they enhance cash flow management and financial forecasting. Automated reconciliation ensures accuracy, helping businesses maintain robust financial health.
- Automated compliance and documentation: In the ever-evolving landscape of international trade laws and regulations, automated compliance systems ensure businesses remain compliant. This reduces not only the risk of fines but also avoids shipment delays and customs holdups that can disrupt supply chains.
- Automated reporting and analytics: It’s not just about collecting data but interpreting it meaningfully. Automated systems provide digestible and actionable insights, enabling businesses to continuously refine their strategies and maintain a competitive edge.
- Automated warehouse management: This goes beyond storage optimization. Automated warehouse management systems can also factor in the speed of retrieval based on product demand forecasts, ensuring that high-demand items are easily accessible, thus streamlining the entire pick-pack-ship process.
The role of autonomous mobile robots in logistics optimization
In an era defined by rapid technological advancement, the integration of Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) into logistics is a testament to the intersection of innovation and demand. AMRs, with their self-navigating capabilities, have reshaped the logistics landscape, making operations not only faster but also more efficient. By seamlessly blending into existing infrastructures, they reduce human error, increase productivity, and ensure a smoother flow in supply chain processes.
AMRs also represent a paradigm shift in how we think about warehousing and transportation. As labor shortages become a pressing concern in many parts of the world, AMRs provide a sustainable solution, ensuring that logistics operations remain unhindered. Their adaptability to various environments, be it a bustling warehouse or a complex distribution center, is unparalleled. Here are a few ways that AMRs can support logistics optimization:
- Transportation: Within the vast expanse of a warehouse or distribution center, AMRs excel in transporting goods. Not only can they replace manual cart-pushing, but their advanced navigation systems allow them to detect and avoid obstacles, ensuring safe and seamless movement. Their capacity to be programmed to follow specific routes and schedules means there’s consistency in their operations, minimizing unforeseen disruptions and ensuring timely movement of goods.
- Inventory management: Integrated with modern warehouse management systems, AMRs can autonomously scan, record, and manage inventory levels. Their ability to consistently track the location of items, even during peak operational times, means a reduced risk of misplaced goods. This tight integration ensures real-time, accurate insights into stock levels, aiding in demand forecasting and replenishment strategies.
- Automated tracking and monitoring: Beyond just transporting goods, AMRs are equipped with sensors and cameras that provide real-time monitoring. This capability ensures that any deviations from expected paths or schedules are immediately flagged. Businesses can then swiftly intervene, ensuring minimal disruption to the supply chain and enhancing overall reliability.
- Picking and packing: The modern AMRs, when integrated with robotic arms and advanced gripping mechanisms, can autonomously select and package items. This reduces the margin of human error, ensuring customers receive the correct products in their orders. By streamlining this process, businesses can process a larger number of orders in a shorter time span, catering to the demands of e-commerce-driven markets.
- Load balancing: Ensuring that goods are stored efficiently is paramount in logistics. AMRs have the capability to determine the optimal placement of items based on weight, size, and frequency of access. This strategic load balancing maximizes space usage, facilitates quicker retrieval, and ensures structural safety within storage racks.
- Automated warehouse management: Advanced AMRs play a pivotal role in warehouse operations. Their capability to efficiently store and retrieve goods based on AI-driven algorithms means warehouses can operate at peak efficiency around the clock, making the most out of available space and resources.
- Flexibility: One of the standout features of AMRs is their adaptability. With changing business dynamics, AMRs can be swiftly reprogrammed to cater to new operational needs, be it a sudden influx of a particular product or the incorporation of new warehouse sections.
- Cost-effective: While the initial investment in AMRs can be significant, the long-term returns in terms of productivity and efficiency are substantial. By automating repetitive tasks, businesses can redirect their human workforce to more value-added roles. Moreover, by cutting down on manual errors and increasing operational speed, AMRs often lead to notable cost savings in the long run.
The Innovation Trends Advancing Logistics Optimization
As COOs and CSCOs ramp up their investments in digital transformation, logistics innovation is rapidly advancing. This momentum is driven not just by enduring labor shortages but by a multifaceted set of challenges. The push to bring operations closer to customers through reshoring or nearshoring, the complexities introduced by e-commerce in both B2C and B2B sectors, and the ongoing supply chain disruptions have all nudged operations leaders. They’re now turning to state-of-the-art technologies to enhance throughput, streamline processes, and secure a competitive edge for the long haul. Here are the top innovation trends advancing logistics optimization:
- Autonomous vehicles: AVs offer several benefits in logistics, including improved safety, increased efficiency, lower costs, and enhanced flexibility. They can reduce accidents caused by human error, optimize routes and delivery times, operate 24/7, and respond quickly to changing demands. Examples of automated vehicles in logistics include self-driving trucks that transport goods without a human driver, delivery robots that can navigate sidewalks and cross streets safely, drones for package delivery to remote or hard-to-reach locations, and autonomous forklifts in warehouses that increase productivity and reduce the risk of accidents. At Vecna Robotics, we released the market’s first co-bot pallet jack. The CPJ is designed to move nimbly in cramped spaces and is optimized for tasks such as replenishment, waste and dunnage retrieval, consolidation of empty pallets, totes and carts, pick-to-packout, and other similar workflows.
- Internet of Things: IoT in logistics offers real-time tracking, monitoring, and analysis of goods and vehicles. The benefits of IoT in logistics include improved efficiency, cost reduction, enhanced customer service, and increased visibility and control over the supply chain. Examples of IoT in logistics include smart sensors that monitor temperature, humidity, and shock during transportation, GPS tracking devices that provide real-time location updates, and predictive analytics that help identify potential issues before they occur. Additionally, IoT can help optimize delivery routes, reduce fuel consumption, and minimize vehicle downtime, resulting in faster, more efficient, and cost-effective logistics operations.
- Blockchain: Blockchain technology provides secure, transparent, and decentralized tracking and verification of goods and transactions. This increases efficiency, reduces costs, enhances security, and improves trust and accountability in the supply chain. Examples of blockchain in logistics include secure tracking of goods through the entire supply chain, automatic verification of customs documents, and smart contracts that automate payment and settlement processes. Blockchain can also help prevent counterfeiting and fraud, enable faster and more efficient cross-border transactions, and improve the overall transparency and accountability of logistics operations. Overall, blockchain technology offers significant potential to transform the logistics industry by improving efficiency, security, and transparency in supply chain operations.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Artificial intelligence (AI) offers logistics companies predictive and prescriptive analytics, automated decision-making, and intelligent optimization of supply chain operations. Benefits include increased efficiency, improved accuracy, reduced costs, and enhanced customer service. Examples of AI in logistics include predictive maintenance of vehicles and equipment, intelligent routing and scheduling of shipments, automated inventory management, and chatbots that provide real-time customer support. AI can also help optimize warehouse layouts, improve last-mile delivery, and enable better risk management and contingency planning.
- 3D Printing: 3D printing technology enables the on-demand production of spare parts, prototypes, and customized products, resulting in reduced lead times, lower inventory costs, and improved supply chain flexibility. The benefits of 3D printing in logistics include reduced waste, increased customization, enhanced speed-to-market, and lower transportation costs. Examples of 3D printing in logistics include the production of spare parts on-site, customized packaging, and the creation of prototypes and samples for product testing. Additionally, 3D printing can help reduce the carbon footprint of logistics operations by minimizing the transportation of products and materials. Overall, 3D printing provides more sustainable, cost-effective, and flexible solutions for production and supply chain operations.
- Robotics: Robotics technology is used to automate warehouse and distribution operations, such as order fulfillment, material handling, and warehouse management. The benefits of robotics in logistics include reduced labor costs, increased speed and accuracy, improved safety, and enhanced productivity. Examples of robotics in logistics include autonomous mobile robots that transport goods within warehouses, robotic arms that automate order picking and packing, and drones that can deliver packages to remote or hard-to-reach locations. Additionally, robots can help optimize warehouse layouts, reduce inventory costs, and improve the overall efficiency of logistics operations.
- Advanced Analytics: Logistics companies use advanced analytics to gain real-time, data-driven insights that enable better decision-making and optimization of supply chain operations. The benefits of advanced analytics in logistics include increased efficiency, reduced costs, improved customer service, and enhanced visibility and control over the supply chain. Examples of advanced analytics in logistics include demand forecasting, predictive maintenance, route optimization, and inventory optimization. Additionally, analytics can help identify potential issues before they occur, such as delays in transportation or stockouts, enabling logistics managers to take proactive measures to prevent them.
- Augmented Reality (AR): Augmented reality (AR) may seem unexpected in logistics but its real-time visualization and interaction with physical objects and data offer the benefits of improved accuracy, reduced error rates, enhanced safety, and increased efficiency. Examples of AR in logistics include pick-by-vision systems that guide warehouse workers in selecting and packing items, remote maintenance and repair assistance using AR-enabled glasses or smartphones and real-time visualization of product assembly or packaging instructions. Additionally, AR can help optimize warehouse layouts, improve quality control, and enhance the training and onboarding of logistics personnel.
- Cloud computing: In logistics, cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing resources, data storage, and software applications from any location with an internet connection. This helps increase scalability, reduce capital expenditure, enhance collaboration, and improve data security. Examples of cloud computing in logistics include cloud-based transportation management systems (TMS) that provide real-time visibility into shipment status and optimize routing, cloud-based warehouse management systems (WMS) that automate inventory management and order fulfillment and cloud-based analytics platforms that provide real-time insights into supply chain performance. Additionally, cloud computing can help reduce the need for on-premise IT infrastructure, enabling logistics companies to focus on core business operations. All Vecna Robots are cloud-enabled solutions allowing for real-time remote monitoring and software updates.
- Electric vehicles: Electric vehicles (EVs) are a sustainable and cost-effective alternative to the fossil fuel-powered vehicles traditionally used in logistics. They help reduce greenhouse gas emissions, lower fuel and maintenance costs, and increase operational efficiency. Examples of EVs in logistics include delivery vans, trucks, and even drones that use electric power to transport goods over shorter distances but some logistics companies have begun implementing electric-powered warehouse equipment such as forklifts and pallet jacks, further reducing their carbon footprint.
Automation can be a powerful tool for logistics optimization, but it is important to consider the costs and benefits of each automation solution before implementation. It is also important to ensure that the automated systems are properly integrated with existing systems and processes and that the necessary training and support are provided for employees who will be using the new systems. With proper implementation, automation can greatly improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer service for businesses that rely on the transportation and delivery of goods.
In particular, AMRs can improve logistics optimization by increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing customer service. However, it is important to consider that the specific workflows that require automation are highly repeatable tasks, that are considered low-value human work, and that have already been proven by existing automation technologies. This will ensure that your automation investment will deliver the intended value and will scale properly with the needs of your operation.
Vecna Robotics has a wide range of AMR pallet handling solutions designed to optimize logistics operations with automation and improve overall throughput. Vecna Robotics has automation solutions tailored for the most demanding warehouse workflows. For more information about how to get your facility started with our automation solutions, go to our From No Bot to Robot page, or contact us today to schedule a consultation with a material handling automation expert.





